See Gigabit Ethernet.
See Fast Ethernet.
Audio Engineering Society standard for transport of digital audio signals.
For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AES3.
A single audio signal. Audio channels on CobraNet have a 48 kHz sampling rate and may be 16, 20 or 24 bit resolution. Multiple audio channels may be carried in a bundle.
A low bit rate form of communication during which one device tells another device if it is capable of full- or half-duplex operation and whether to connect at 10MB or 100MB bit rates.
Bootstrap Protocol. A UDP protocol used by a network client to obtain its IP address automatically. This process is performed when the unit is starting up.
A special type of multicast addressing where data is unconditionally received by all DTEs within a network domain.
The basic network transmission unit under CobraNet. Up to 8 audio channels may be carried in a bundle.
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box with sixteen digital audio inputs and outputs (AES3 and S/PDIF compatible).
Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box with sixteen line-level inputs.
Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box with sixteen line-level outputs.
Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box, designed to work with the NION.
![]()
Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box with eight mic/line-level inputs.
Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box, designed to work with the NION.

Features:
Configurable Audio Bridge. Audio break-out box with eight line-level outputs.
Features:
Inexpensive unshielded twisted pair (UTP) data grade cable.
It is very similar to ubiquitous telephone cable, but the pairs are more tightly twisted. CAT5 cable runs are limited to 100 meters due to attenuation considerations.
Shielded CAT5 is also available, but is less widely used due to its greater cost and run distance limitations.
A range of amplifiers from Crest Audio. Below is a picture of the Ci 20 X 8.
![]()
Features:
A range of amplifiers from Crest Audio. Below is a picture of the CKi 200s.

Features:
A combination of hardware, software, and protocols which distributes digital audio over Ethernet networks. CobraNet supports switched Ethernet networks. CobraNet uses standard Ethernet packets and network infrastructure.
A device in compliance with the CobraNet specification for transmission and/or reception of digital audio and associated sample clock.
A monitoring, troubleshooting and maintenance tool for CobraNet networks. It uses a standard Ethernet network interface card (NIC) to connect to the network. The application discovers devices and displays status information for each of them. It also allows you to configure devices and perform firmware upgrades.
If you have installed DISCO, you can refer to the user manual for information on how to use the software. It is installed in the same folder as the program. Also see http://www.cobranet.info/downloads/disco.
A CobraNet device on the network supplying a master clock. A Conductor arbitration procedure ensures that at any time there is one and only one Conductor per network.
ControlManager provides a platform for MediaMatrix control systems. It can be custom configured to monitor and control multiple NWare projects, consisting of NIONs, CABs, amplifiers, and other devices. Additionally, it can also monitor and control 3rd party devices using SNMP and execute Python scripts.
ConMan is delivered preinstalled on nControl units.
A cable that can be used to directly connect two network devices without a switch, hub, or router, if neither of the devices supports automatic crossover. The input signals from one connector are mapped to the output signals of the other, which allows for full-duplex communication.
A one-gang Decora panel with four programmable virtual rotary controls and status LEDs. It uses the PASHA/XControl protocol to communicate with the NION hardware.
![]()
Features:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A one-gang Decora panel with four programmable buttons and status LEDs. It uses the PASHA/XControl protocol to communicate with the NION hardware.
![]()
Features:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A system for automatically assigning network settings to devices on an IP network. A single DHCP server can assign network settings, including IP address, subnet mask, default gateway etc. to other devices on the network as soon as they power up.
Dante Legacy Module. A networking module installed in NIONs and CAB 4ns to allow audio to be transported across a network.
An alternative system to CobraNet. For more information, refer to the Audinate website.
Domain Name System. A system that translates human readable names for devices on a network into IP addresses. For example, myserver could be equivalent to 192.168.1.42.
Digital Signal Processing. The processing of electronic (audio) signals for a particular application. As part of the processing, the signals may be amplified or filtered, for example.
The MediaMatrix NION contains a number of Digital Signal Processors (DSPs), which are capable of processing many audio signals simultaneously.
In order to specify the DSP you want to perform on audio signals, you need to build a design in NWare using devices from the DSP part of the devices tree.
Data Terminal Equipment. Any network device that produces or consumes data.
A communication system for devices that can operate in both directions at the same time (full-duplex), or in only one direction at a time (half-duplex).
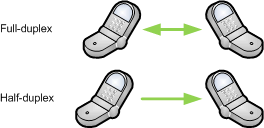
Before CobraNet devices establish a link between each other, a process called auto-negotiation takes place. The devices establish whether half- or full-duplex communication is possible, and the bit rate to use.
Note: CobraNet must operate on a full-duplex network. For more information, see Connections.
A Local Area Network (LAN) protocol that transmits information between computers at speeds of 10 Mbps (megabits per second). It is one of the most widely implemented LAN standards.
An Ethernet multi-port repeater. A data signal arriving in any port is electrically regenerated and sent out all other ports on the hub. An Ethernet hub does not buffer or interpret the data passing through it.
Note: For professional systems we recommend using Ethernet switches in place of hubs. Hubs are considered to be largely obsolete.
A newer version of Ethernet, also known as 100BASE-T. It supports data transfer rates of 100Mbps. CobraNet operates on a Fast Ethernet network.
A labeled wire endpoint. Allows signals to be transferred between devices in different parts of a design (within a page, between pages, between devices on the network, and so on) without there being a graphical wire connection.
In the example below, the output from a mixer device is connected to a flyoff called Flyoff1.
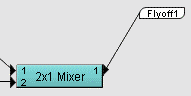
In another part of the design, a second flyoff is also labeled Flyoff1 . Connecting this flyoff to the meter allows the signal to flow from the mixer device to the meter.
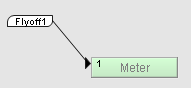
For more information, see Working with flyoffs in the NWare User Guide.
Gigabit Ethernet is a newer version of Ethernet, also known as 1000BASE-T. It supports data transfer rates of 1000 Mbps (1 gigabit).
A 4-digit ID that uniquely identifies a CAB on the CobraNet network. The ID is specified using switches on the physical CAB device.
A networked audio input and output node that supports both CobraNet and Dante protocols. The device provides a serial interface (RS-232 or RS-485), as well as GPIO interfaces, for control of locally connected devices.

The F-DCM features two mic/line inputs on XLR and Euro connectors, each with 48V phantom power, and two line level outputs on Euro connectors. The line output channels are also amplified by dedicated 25 watt power amplifiers for driving local near field monitors though the screw terminal connectors on the rear of the unit.
A networked audio input and output node that supports both CobraNet and Dante protocols. The device provides a serial interface (RS-232 or RS-485), as well as GPIO interfaces, for control of locally connected devices.
![]()
The H-DCM features two mic or line inputs on XLR or Euro connectors, each with 48V phantom power, and two line level outputs on Euro connectors.
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection. A protection system designed to prevent copying of digital video and audio. The system also prevents playback of content on unauthorized devices, or devices modified to copy HDCP content.
For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HDCP.
A device for connecting multiple Ethernet devices together, making them act as a single network segment. The term hub can refer to a repeater hub (which forwards packets received on any port to each of the other ports) or a switching hub (which only forwards received packets to the appropriate port, based on the address of the packet).
Note: For professional systems we recommend using Ethernet switches in place of hubs. Hubs are considered to be largely obsolete.
NWare:Kiosk or just Kiosk is an NWare client that allows a user to make adjustments to some control values in an audio system, such as volume levels or preset recall, but does not allow any changes to the design of the system.
Kiosk offers a number of benefits, including:
A 16x9 ratio, high definition touch screen control panel for controlling MediaMatrix systems.

The device runs an embedded version of NWare Kiosk and allows the user to control a project designed in NWare.
Kiosk 180HD provides several mounting options, including surface, panel, flush and general VESA mounting.
A web-based interface for controlling NWare projects. It provides similar functionality to Kiosk, but is optimized for both touch devices, like iPads, iPhones and Android tablets, and PC-based browsers.
You can run Kiosk2Go on a NION, nControl or nTouch 180, and you can also use it with an emulated project.
A means for making multiple Ethernet links act as a single, higher capacity, fault tolerant link. It can be used to link multiple Ethernet switches together, for example. Link aggregation is also known as trunking.
Megabits per second. A measure of data transfer speed.
A two port device that accepts one type of media on one port and a different type of media on the other. Common Ethernet media types are twisted pair, multimode fiber and single mode fiber. Some hubs and switches include media conversion via plug-in modules.
A fusion of spanning tree protocol and link aggregation. Eliminates loops while creating higher capacity, fault tolerant links among interconnected (meshed) switches.
A configuration for a mixing console where the output from a particular device contains everything except the input from that device. It is designed to prevent echoes or feedback from reverberating or howling and squealing through the broadcast or sound reinforcement system.
A serial communications protocol for programmable logic controllers (PLCs). One version is called Modbus RTU, which includes a CRC error checking mechanism.
Data which is multicast is addressed to a group of DTEs (or all DTEs) on a network. All DTEs receive multicast addressed data and decide individually whether the data is relevant to them.
An Ethernet switch is typically not able to determine an appropriate destination port or ports for multicast data and thus must send the data out all ports simultaneously, just as a Ethernet hub does.
Tip: Unicast addressing, where data is addressed to a specific DTE, should be used in place of multicast addressing whenever possible. Multicast addressing uses bandwidth network-wide, since all DTEs have to decide whether multicast data is relevant to them.
A bundle that supports a one-to-many routing of data on the network. Ethernet multicast addressing is used to deliver a multicast bundle.
Note: As a multicast bundle consumes bandwidth network-wide, use of this delivery service must be rationed on a network.
A fiber-optic cable commonly used in data communications and short haul telecommunications. A multimode fiber is constructed using two types of glass arranged in a concentric manner. Two sizes of fiber are available:
The standard for transmission of 100Mbit Ethernet over 62.5/125um multimode fiber is called 100BASE-FX. Multimode fiber and its associated transceivers are fairly economical.
Refer to the fiber-optic hardware manufacturer's documentation for information on distance limitations and fiber types.
An industrial network PC server running ControlManager application software. ControlManager provides a platform for MediaMatrix control systems. It can be custom configured to monitor and control multiple NWare projects, consisting of NIONs, CABs, amplifiers, and other devices. Additionally, it can also monitor and control 3rd party devices using SNMP and execute Python scripts.
![]()
After nControl has been installed and given initial configuration settings, it is managed using NWare.
Note: nControl units host projects for control and monitoring, but do not have any DSP capability.
Neighborhood Discovery Protocol. An IP6 protocol that can be used to discover network devices and assign them IP addresses. For more information, see Neighborhood Discovery Protocol.
The longest cable distance between any two DTEs on the network.
The physical and logical relationship of nodes in a network; networks typically have a star, ring, tree or bus topology, or some combination.
Network Interface Card. An expansion board inserted into a computer in order to connect the computer to a network. Typically, NICs are designed for a particular type of network and media, although some can serve multiple networks.
Digital audio processor. Compatible with the CAB audio break-out boxes (CAB 4n, CAB 16d, etc.).
![]()
Features:
A processing location. A node can be a computer, a switch, a CobraNet device, or any other device that has a unique network address.
A touch screen control panel for controlling MediaMatrix systems.

The device runs an embedded version of NWare Kiosk and allows the user to control a project designed in NWare.
In addition to this functionality, nTouch 180 runs ControlManager application software. ControlManager provides a platform for MediaMatrix control systems. It can be custom configured to monitor and control multiple NWare projects, consisting of NIONs, CABs, amplifiers, and other devices. Additionally, it can also monitor and control 3rd party devices using SNMP and execute Python scripts.
nTouch 180 provides several mounting options, including surface, panel, flush and general VESA mounting.
A 16x9 ratio, high definition touch screen control panel for controlling MediaMatrix systems.

The device runs Kiosk2Go, plus an embedded version of NWare Kiosk. It allows the user to control a project designed in NWare.
In addition to this functionality, nTouch 180HD runs ControlManager application software. ControlManager provides a platform for MediaMatrix control systems. It can be custom configured to monitor and control multiple NWare projects, consisting of NIONs, CABs, amplifiers, and other devices. Additionally, it can also monitor and control 3rd party devices using SNMP and execute Python scripts.
nTouch 180HD provides several mounting options, including surface, panel, flush and general VESA mounting.
A wall-mounted control panel for controlling MediaMatrix audio systems.

The unit has a touch-sensitive screen for selecting options from an audio control project, which has been designed in NWare. It also has a knob for adjusting individual settings, like volume, and selecting options.
The nTouch 60 works in conjunction with an nControl unit or an nTouch 180 unit, which hosts the Kiosk pages from the NWare project.
A CobraNet interface panel with both XLR and TRS mini jack connectors. The nWall 2.0 has two microphone/line level input channels. The nWall 0.2 has two analog line level output channels. The nWall 1.1 has two analog line level input channels and two analog line level output channels.

Software for designing networked audio solutions using MediaMatrix products, including NIONs and CAB 4ns.
Features:
An extended version of NWare that was used in versions prior to 1.5.1 for SNMP monitoring and configuration of ControlManager.
With the introduction of nControl, NWare 1.5.1 and subsequent releases, use of NWare++ is no longer required. All the configuration options are available when you run the standard version of NWare.
A paging system that works in conjunction with a MediaMatrix audio system.
MediaMatrix serves as the central processing unit, controlling the entire system from signal routing to the paging system. The PageMatrix system provides multiple paging stations that are easily configured to just about any page/zone requirement.
The PageMatrix hardware components include the 2-rack space PageMatrix Controller and three types of paging stations.
![]()

A Windows service that discovers MediaMatrix devices on the network. The list of available devices is shown on the NWare Remote Log tab.
For detailed information on Pandad, refer to the CobraNet Networking Guide or Dante Networking Guide.
The MediaMatrix serial handling adapter. It is a remote control protocol that provides external serial command and read-back of designer selected controls in a NION project.
Note: PASHA can only be used with the RS-232 or RS-422/RS-485 serial ports at the rear of the NION.
A system for transferring electrical power over an Ethernet cable, alongside data. It allows devices to be connected using just a single Ethernet cable, rather than an Ethernet cable and a separate power cable.
An open source scripting language that has been ported to run on many platforms. Python version 2.4 is supported on NioNodes, nControl nodes and nTouch 180 nodes.
In NWare, Python script functions can be authored by the designer to implement custom control interactions. The functions are added to the design using device blocks. Whenever any of the controls wired to the inputs of the blocks change, the functions are run.
For a list of supported modules, see Support for Python modules.
The home page for Python is http://www.python.org/. The Python 2.4 documentation is available here.
A free, Windows-based Python development package, called ActivePython, is available from ActiveState at http://www.activestate.com/.
Remote Access Terminal Control. A command-line based protocol that allows a remote client program to set and get the control values in an NWare project. The remote client communicates with the project via a TCP network connection to any one of the NioNodes or nControl nodes in the project.
Remote Access Terminal Control version 2. An improved version of RATC. RATC2 introduces shortened commands and several extra functions. One of the most useful improvements for third-party programmers is the Change Group Scheduling feature, which can be configured to automatically send changed values without being polled.
RATC2 RAW is a variant of the RATC2 protocol. It allows you to access controls in a project using control aliases in the same way as RATC2, but the aliases are defined automatically. You do not need to manually specify them for each control in NWare.
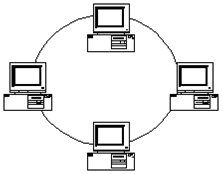
A network topology in which all nodes are connected in a closed loop.
An object containing a group of devices from an NWare project. Devices in your design are allocated to roles (either manually, or automatically by NWare). Roles are then assigned to MediaMatrix hardware devices for processing during deployment.
A device that converts the rotary motion or angular position of a knob control into electrical signals. These signals can, in turn, be passed to a device, such as a NION, to control devices in an NWare project.
For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotary_encoder.
Relatively Unique ID. Each control added to an NWare project has a RUID. RUIDs are displayed on the Inspector tab. To display the Inspector tab, click User Preferences on the Tools menu, then select Show Inspector on the Advanced tab of the User Preferences dialog box. Restart NWare.
Each type of media has a limitation in the length of a point-to-point run between two devices. When maximum run length guidelines are exceeded it may not be possible to establish a valid network connection or data may be corrupted. Longer distances can be achieved by upgrading the media or using multiple runs in series.
Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format or Sony/Philips Digital InterFace. A data link layer protocol (and standard that covers the specification of the physical layer) for carrying digital audio over an IP network.
For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/S/PDIF.
A fiber optic cable built from a single type of glass. Data is carried over single mode fiber in the coherent light produced by a laser.
Single mode fiber systems are able to achieve much greater transmission distances than multimode fiber systems, but while a single mode fiber cable costs approximately the same as a multimode cable, the cost of the optical transmitters and receivers is significantly more.
There is no official standard for carrying Ethernet over single mode fiber. Single mode fiber systems each have their own run length limits.
Refer to the fiber-optic hardware manufacturer's documentation for information on distance limitations and fiber types.
A standard for electronic email transfer across the internet.
Simple Network Management Protocol. A standard network protocol used to monitor the status of devices on a network and configure their settings. For more information, see Wikipedia SNMP definition.
An IEEE standard protocol (802.1D) allowing detection and elimination of loops in Ethernet networks. Spanning tree protocol is implemented on most managed switches.
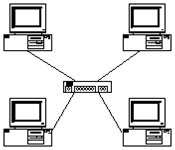
A network topology in which all nodes are connected to a central network device such as a hub or switch.
A logical division of a network. Subnets are used to divide a network into smaller, more easily managed sections.
Routers are used to manage traffic on subnets and act as borders between them.
For more information, see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subnetwork.
Examines addressing fields on data arriving at each port and attempts to direct the data out the port or ports to which the data is addressed. Data may be buffered within the switching hub to avoid the collision condition experienced within a hub. A network utilizing switching hubs realizes higher overall bandwidth capacity as data may be received through multiple ports simultaneously without conflict. Switches are full-duplex devices. A network utilizing switches to connect network segments is referred to as a switched network.
A computer industry standard network communications protocol which is generally used to connect remote users to a host computer using a text-based interface. The user can then control certain functions on that host computer. Telnet works over both local area networks and the Internet.
MediaMatrix Telephone Paging Unit with two ports.

Features:
MediaMatrix Telephone Paging Unit with four ports.

Features:
See link aggregation.
User Datagram Protocol. A member of the Internet Protocol Suite. This protocol allows messages (datagrams) to be sent by applications to other hosts on an IP network. No prior communications, transmission channels or data paths are required before transmission.
Data which is unicast is addressed to a specific DTE. A switching hub may examine the unicast address field of the data and determine on which port the addressed DTE resides and direct the data out only that port. Delivery of an e-mail message is an example of unicast data addressing.
Tip: Unicast addressing, where data is addressed to a specific DTE, should be used in place of multicast addressing whenever possible. Multicast addressing uses bandwidth network-wide, since all DTEs have to decide whether multicast data is relevant to them.
A unicast bundle supports a one-to-one routing of audio on the network. Ethernet unicast addressing is used to deliver a unicast bundle.
Refers to any data transmitted onto a network by non-CobraNet devices. On a switched network, unregulated traffic is not generally a problem, unless there is a large amount of it and it causes the network to become overloaded.
Uninterruptable Power Supply. Also known as a Continuous Power Supply (CPS) or battery backup. This device maintains a constant supply of power to equipment, even if utility power is unavailable. The UPS will supply power for a limited time, until the utility power is restored, or an alternative power generation system has been activated.
An HDBaseT extender comprising transmitter (VCAT-HD-T) and receiver (VCAT-HD-R).
VCAT-HD delivers HDMI video signals and IR and RS-232 control signals over a single STP cable. The maximum transmission distance is 70 meters (230 ft) with CAT5e/CAT6 cable.

Virtual LAN. A set of devices on the network that have been placed in the same logical group, even though they may not be in the same physical location. Devices in the VLAN communicate with each other as if they were part of the same broadcast domain.
In audio networking, VLANs can be used to logically separate general network traffic from audio (CobraNet) traffic, and ensure the CobraNet traffic is transmitted and received in a timely fashion.
A full HD video scaler switcher. The device scales and switches any HDMI, VGA, YPbPr, C-Video or S-video video signal to HDMI up to 1080P. It is controllable via buttons on the front, the IR sensor and the RS232 port.

A full HD video scaler switcher. The device scales and switches any HDMI, VGA, YPbPr, C-Video or S-video video signal to HDMI up to 1080P. It is controllable via buttons on the front, the IR sensor and the RS232 port.

A full HD video scaler switcher. The device scales and switches any HDMI, VGA, YPbPr, C-Video or S-video video signal to HDMI up to 1080P. It is controllable via buttons on the front, the IR sensor and the RS232 port.

A slang term for a type of power supply that is embedded in an over-sized AC plug. These devices are typically used when the device they supply does not include a power supply in the case.

Wall-mounted remote control panel. Allows a user to control the features of a MediaMatrix audio system using simple controls.
The device is fully-configurable, so the knob and buttons perform functions specified by the designer. As an example, the user could select pre-recorded messages for playback using the buttons and control the volume using the knob.
There are three XControl variants: the XControl 4x4 (shown below), the XControl 4L and the XControl 4S.

A wall-mounted control panel for controlling MediaMatrix audio systems.

The unit has capacitive touch buttons for selecting the audio source, zone and level, as well as muting the output and confirming a menu choice or setting change (Enter button). There is a two color LCD display for presenting information to the user.
Note: Currently, the xControl LCD is limited to controlling a maximum of 4 input sources and 4 zones.
The xControl LCD works in conjunction with a NION, which communicates with the unit via an EIA-485 connection.
A digital interconnection system for NIONs. NIONs connected together via XDAB are referred to as an XDAB cluster.
There is one XDAB master that provides the audio clock to all other devices in the cluster. The other devices in the cluster are XDAB slaves.
Note: XDAB is available on NION n3 and N6 models, but not nX or nE models.